Good morning, readers!
In Russia, Vladimir Putin signed a new law allowing police to freeze citizens’ bank accounts for up to 10 days without a court order. While framed as an anti-fraud measure, the law gives police a fast and legally deniable way to cut off dissent that could leave civil society unable to pay rent, receive donations, or fund their activism.
Meanwhile, Iranian officials seized the homes, assets, and bank accounts of more than 20 Bahá’i families in Isfahan, notifying some only by text message. This financial repression of a religious minority group reflects how the regime politicizes money to exclude vulnerable groups from financial freedom and the rights that flow from it.
In freedom tech news, accessibility leaped forward with two major launches: Bitchat, a Bluetooth-based messaging app built for communication without Internet access, is now live on the Google Play Store, and Obscura VPN, a strong privacy-protecting VPN, was approved on Apple’s App Store. Both additions make permissionless and offline freedom technologies easier to install and update, lowering barriers for their use under autocratic regimes.
We end with highlights from HRF’s Freedom Tech portion of the SALT investment conference in Jackson Hole, Wyo., where human rights defenders and dissidents explored how Bitcoin is being used as a tool for peaceful protest, a hedge against hyperinflation, and a new way to conduct philanthropy.
Now, let’s get into the news.
Global News
Russia | Grants Police Power to Freeze Bank Accounts
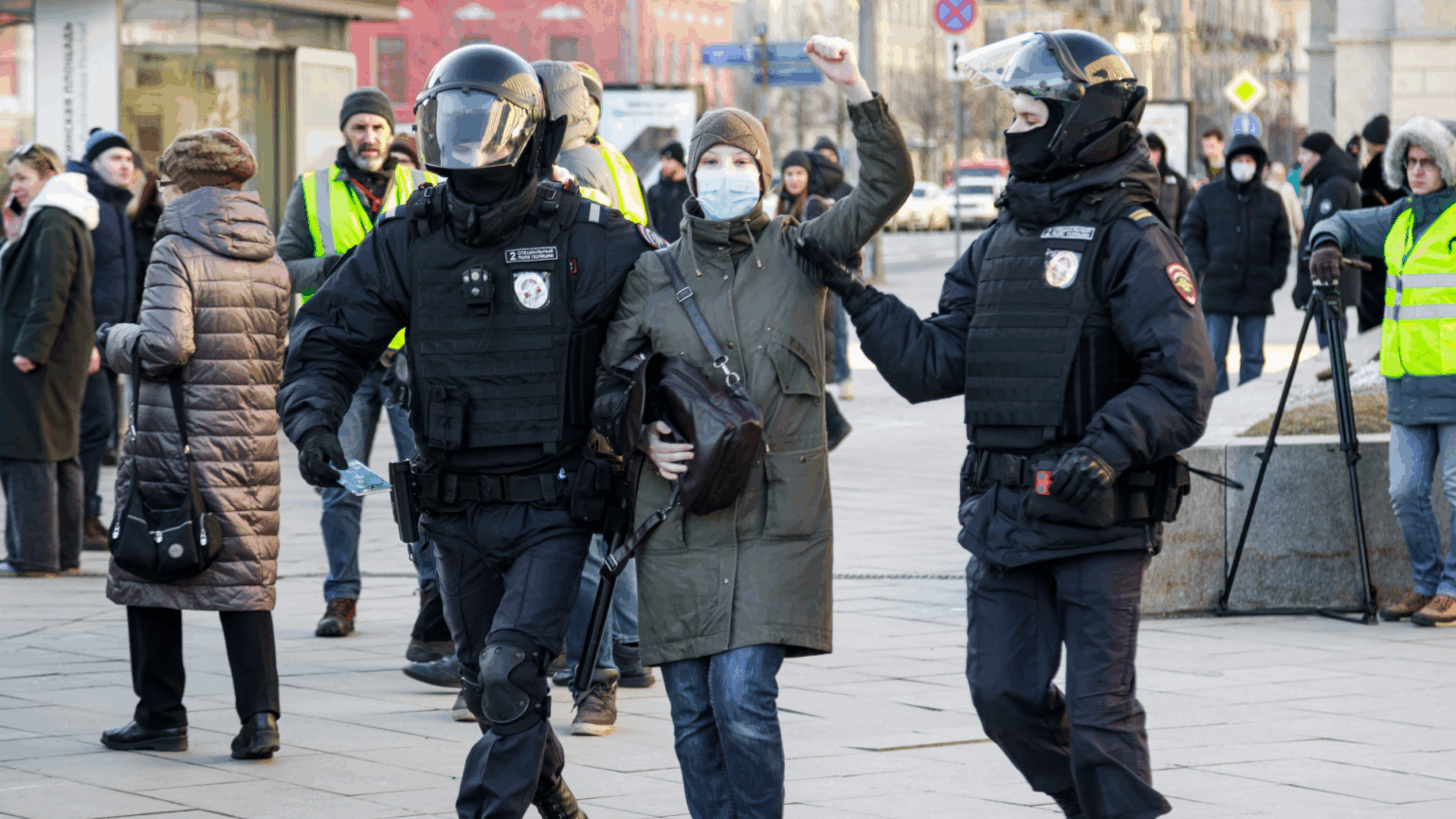
Dictator Vladimir Putin signed a new law granting police authority to freeze Russian citizens’ bank accounts without a court order. Officers can suspend accounts for up to 10 days on suspicion of criminal activity, expanding powers previously limited to property seizures. Banks and payment providers must also hand over citizens’ account records within three days, or within 24 hours if the request is made electronically. The Kremlin claims these measures will help reduce cybercrime and fraud, insisting the law will not infringe on the rights of “law-abiding” citizens. But, “the legislation provides no specific list of crimes that qualify for account freezes and fails to outline key procedural safeguards,” said Yuliy Tai, senior partner at the Bartolius Law Office. The risk is clear for human rights defenders and journalists: officials now have a faster, legal mechanism to cut off financial access. The ability to transact, pay rent, receive donations, and fund protests is existential.
Iran | Confiscates Property and Bank Accounts of Bahá’i Minorities
Last week, Iran’s oppressive clerical regime seized the homes, vehicles, and assets of 20 families from Iran’s Baháʼí community, the country’s largest non-Muslim religious minority. Officials seized assets under Article 49 of Iran’s constitution, a provision meant to recover illegally obtained wealth. But the Bahá’i International Community (BIC) accused officials of misusing the law without evidence, due process, or transparency to target citizens solely for their faith. Families report frozen bank accounts, blocked transactions, and court files withheld from the official judicial system, leaving them defenseless. Officials even notified some families of the confiscations via text message. This is part of a broader effort of persecution: Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei has issued a fatwa instructing Iranians to shun the Bahá’i socially and economically. These actions highlight how politicized money enables state-led exclusion, as property seizures and financial repression are used against religious minorities.
Syria | Plans to Drop Two Zeros from Currency
Syria’s central bank announced it will revalue the pound in December, removing two zeros and issuing new banknotes. Officials present the move as an effort to restore confidence after the currency lost more than 99% of its value since 2011, collapsing from 50 to 10,000 pounds per US dollar. Today, families carry bags of 5,000-pound notes to buy basic goods, and the economy has largely dollarized. The revaluation also reflects the regime’s attempt to bring an estimated 40 trillion pounds circulating outside the banking system under greater state oversight. “Issuing new notes would grant the government better oversight over the cash in circulation,” remarked a Syrian banking official. However, removing two zeroes from the pound is nothing more than a facelift: it may ease cash handling, but it does nothing to address Syria’s deep monetary dysfunction, reliance on foreign currency, or lack of trust in state institutions.
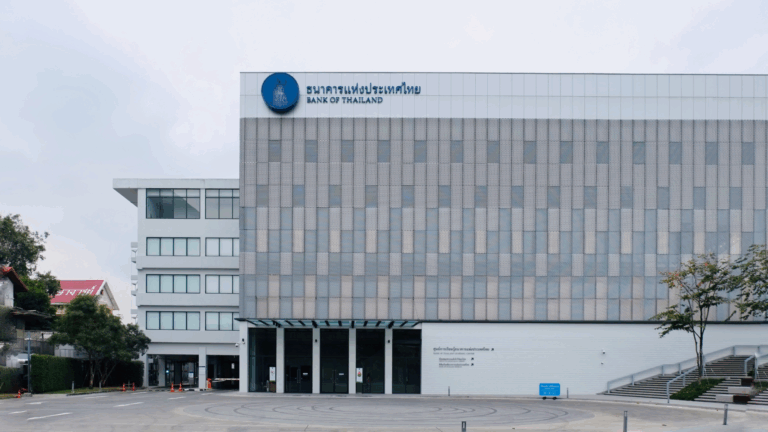
Thailand | Central Bank Caps Daily Transaction Amounts
The Bank of Thailand announced new financial rules limiting daily money transfers to 50,000 baht ($1,400) by the end of 2025. Officials say the cap will protect Thais from online scams. More accurately, it restricts how much citizens can freely move their own money under the guise of consumer protection. Vulnerable groups such as the elderly and children will face additional restrictions, while banks may ease restrictions for established customers. For individuals, nonprofits, and activists, daily transfer ceilings risk disrupting legitimate transactions and could provide the Thai regime with another tool of financial control. Normalizing these limits lets the central bank expand its authority over individuals and civil society’s economic activity, a tactic Thailand’s government increasingly uses to suppress dissent.
Bank for International Settlements | Proposes Self-KYC for Non-Custodial Wallets
Economists at the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) authored a paper proposing a new framework that would ban coins passing through non-custodial wallets from being accepted by regulated exchanges. The paper outlines a system of “compliance scores” attached to each coin, where only funds originating from verified wallets would be considered “clean” and eligible for conversion into fiat. Coins linked to privacy tools or self-custody wallets could be excluded entirely. The BIS frames this as creating a “culture of duty of care,” shifting responsibility to individual users to avoid “tainted” coins. But the BIS seemingly ignores populations that live under dictatorships and misses that dissidents, nonprofits, and civil society depend on financial privacy to protect donors, make secure transactions, and move funds across borders without fear of retaliation from authoritarian states.
Bolivia | Deteriorating Economy Defines Elections
Bolivia’s Aug. 17 election ended the nearly two-decade dominance of the Movimiento al Socialismo (MAS) party, with the vote heading to a runoff for the first time between Sen. Rodrigo Paz Pereira and former President Jorge “Tuto” Quiroga. The result reflects deep public frustration amid the country’s worst economic crisis in more than 30 years. Inflation has reached its highest level since 1991, shortages of fuel and basic goods are widespread, and trust in the state has collapsed. For most Bolivians, the election was about daily survival: whether wages hold value, fuel can be bought, and families can afford food. Against this backdrop, many are turning to digital assets as an alternative to the failing financial system, seeking to protect savings, move funds, and transact outside state control. This shift has contributed to a notable rise in Bitcoin activity across Bolivia in 2025.
Recommended Content
Freedom Tech at SALT Investment Conference
Last week, HRF sponsored a dedicated Freedom Tech portion of the SALT Investment Conference, showcasing how Bitcoin and open-source technologies intersect with human rights, activism, and financial freedom. The program featured a mix of keynotes and fireside conversations with global activists, builders, and changemakers. Sessions ranged from Evan Mawarire’s personal story of resisting Mugabe’s dictatorship and hyperinflation in Zimbabwe to conversations on Bitcoin as a peaceful protest with Serbian activist Srdja Popovic and the Anti-Corruption Foundation’s Anna Chekhovich. Watch them here.
Bitcoin and Freedom Tech News
Bitsacco | Adds Support for Lightning Addresses
Bitsacco, a Bitcoin-powered cooperative savings model piloting in Kenya, introduced Lightning Addresses, making it easier for members to receive Bitcoin directly into their personal savings wallets. Bitsacco combines the familiar structure of African Savings and Credit Cooperatives (SACCOs) with Bitcoin Fedimints. This helps local communities pool resources while maintaining greater control over their funds outside traditional banks. Lightning Addresses make Bitsacco far more practical by giving every member a simple, permanent way to receive funds, like an email for Bitcoin. This eliminates the friction of generating new invoices, enabling activists and communities to accept donations or savings contributions instantly, from anywhere in the world, without relying on banks or exposing themselves to censorship.
Bitchat | Launches on Google Play Store
Bitchat, a Bluetooth-based messaging app built by Twitter and Block founder Jack Dorsey, is now available on the Google Play Store. The app lets users send encrypted messages without relying on the Internet or centralized servers, with chats hopping from phone to phone using Bluetooth until they reach the recipient. This design enables communication in areas with poor connectivity or where dictators block conventional platforms. Bitchat’s latest version also introduces geohash-based location chat, where users can join public or private chats by block, neighborhood, city, or even “teleport” anywhere globally. By moving to the Play Store, Bitchat lowers the barrier to entry and ensures more accessible updates. But developers note that due to a required change in the app’s identifier, early adopters who installed the Bitchat APK on Android will need to reinstall the new version. Try it here.
Obscura VPN | Launches on Apple App Store
Obscura VPN, a private and open-source VPN designed for maximum censorship resistance and privacy, officially launched on Apple’s App Store. Developed by former Bitcoin Core developer Carl Dong, the VPN cannot log your network activity by design. It achieves this by never seeing users’ encrypted Internet traffic. Because of this, it is impossible to log activity, even under the coercion of autocratic regimes. Obscura VPN’s arrival on iOS is a big win for mobile privacy and censorship resistance, especially given Apple’s intensive review process. It broadens access for nonprofits, dissidents, and everyday citizens who need secure and discreet Internet access on the go.
Africa Bitcoin Institute | New African Leadership in Bitcoin Research
On Aug. 20, the Africa Bitcoin Institute launched with support from HRF to focus on research, education, and policy engagement around Bitcoin use across the continent. The initiative is led by Anaïse Kanimba, a Rwandan democracy advocate and the daughter of Paul Rusesabagina, who saved 1,268 lives at his hotel during the Rwandan genocide, as depicted in the film “Hotel Rwanda.” The Africa Bitcoin Institute builds on a decade of grassroots Bitcoin adoption in Africa: from Nigeria’s peer-to-peer networks, to Kenya’s use in remittances, to Zimbabweans turning to Bitcoin as a hedge against inflation. It could become a critical counterweight to authoritarian narratives that seek to limit open digital money while promoting state-controlled alternatives like central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
Bitcoin Design | Celebrates Five-Year Anniversary
The Bitcoin Design Community, an HRF grantee composed of an open-source collective of designers, developers, and contributors, is celebrating its fifth anniversary. Since 2020, the group’s efforts have made Bitcoin more accessible and user-friendly through projects like the Bitcoin Design Guide, a resource that helps developers build intuitive and secure wallets. By improving Bitcoin’s usability, the community lowers barriers for human rights defenders, journalists, and everyday users who rely on Bitcoin as a permissionless and censorship-resistant tool for financial freedom. You can read their five-year report to glimpse their full impact across the Bitcoin ecosystem and how they have helped improve the tools used by activists under authoritarian regimes.
bitcoin++ | Scaling Edition in Istanbul
From Sept. 3-5, developers will gather at Salt Galata in Istanbul, Turkey, for the bitcoin++ Scaling Edition. This three-day event will explore how Bitcoin can operate at a global scale while continuing to serve as a tool for financial freedom for those on the margins of the financial system. With new layer twos like Spark and Arkade, innovations like BitVM, and advances in zero-knowledge proofs, the event will explore the latest tech and developers focused on scaling Bitcoin. For those working at the intersection of open-source development and financial freedom, the conference offers a chance to join the conversation on how Bitcoin evolves over the next decade. Learn more here.
Recommended Content
Lightning swaps *are* the connective tissue by Janusz
This article explores how Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is emerging as the interoperability layer for a growing ecosystem of Layer 2 protocols. Layer 2 protocols are application layers to Bitcoin that typically enable faster, lower-cost, and more private payments. While projects like Arkade, Spark, and Fedimints each use different technical approaches in their implementation, they are increasingly integrating Lightning gateways to connect with one another. A highlight came at Baltic Honeybadger in Riga, Latvia, where Arkade powered payments on the back end while users paid via Lightning and other wallets seamlessly. The takeaway: Lightning is evolving from just a peer-to-peer payments network into a bridge that enables different Bitcoin-native systems to interoperate. This trend could make transacting across diverse protocols seamless and invisible to end users, to the benefit of those who rely on Bitcoin for financial freedom. Read the full essay here.